Introduction
Managing printer queues remotely using Windows PowerShell is a critical skill for IT professionals who oversee multiple devices across networks. Instead of walking to each workstation when print jobs get stuck, you can resolve issues from your desk in seconds. This guide shows you exactly how to manage printer queues remotely using Windows PowerShell with proven commands and scripts. Whether you’re supporting a small office or an enterprise network, mastering these techniques will save you hours of troubleshooting time and keep your printing infrastructure running smoothly.
What Is Remote Printer Queue Management?
Remote printer queue management refers to the ability to control, monitor, and troubleshoot printer jobs on network computers without physical access to those machines. Using Windows PowerShell, administrators can view pending print jobs, cancel stuck documents, restart print services, and perform maintenance tasks from any location on the network.
The print queue acts as a waiting line for documents sent to a printer. When multiple users send jobs simultaneously, or when a printer encounters an error, jobs can pile up or get stuck. PowerShell provides powerful cmdlets (command-line tools) that let you interact with these queues programmatically.
This remote capability becomes essential in modern workplaces where IT teams manage dozens or hundreds of printers across multiple floors, buildings, or even locations. Instead of relying on users to restart printers or walking to each machine, you can diagnose and fix issues within minutes using remote PowerShell sessions.
7 Essential Steps to Manage Printer Queues Remotely Using Windows PowerShell
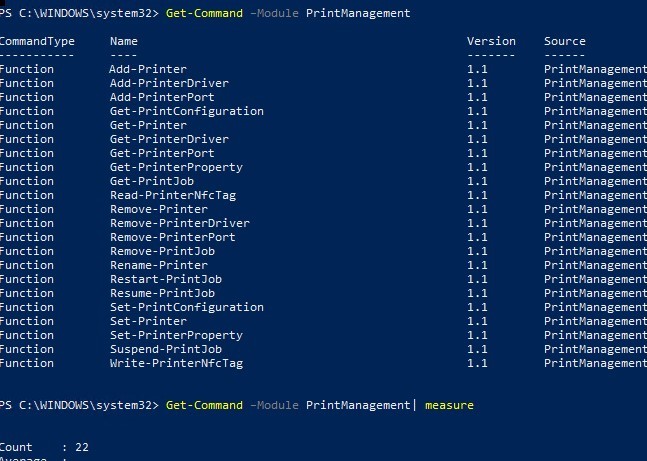
Step 1: Enable PowerShell Remoting on Target Computers
Before you can manage printer queues remotely using Windows PowerShell, you must enable remoting on the computers you want to control.
On each target computer, open PowerShell as Administrator and run:
powershell
Enable-PSRemoting -ForceThis command configures the computer to accept remote PowerShell connections. The -Force parameter skips confirmation prompts. For domain environments, Group Policy can deploy this setting automatically to all machines.
You should also verify that the Windows Remote Management service is running:
powershell
Get-Service WinRMIf the service shows as “Stopped,” start it with Start-Service WinRM.
Step 2: Establish a Remote PowerShell Session
To connect to a remote computer, use the Enter-PSSession cmdlet:
powershell
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName RemotePC01 -Credential Domain\AdminUserReplace “RemotePC01” with the target computer name and provide administrator credentials when prompted. Once connected, your PowerShell prompt will change to show the remote computer name, indicating that all subsequent commands will execute on that machine.
For managing multiple computers simultaneously, use Invoke-Command instead:
powershell
Invoke-Command -ComputerName PC01,PC02,PC03 -ScriptBlock { Get-Printer }This approach lets you run the same command across several machines at once.
Step 3: View All Printers on the Remote System
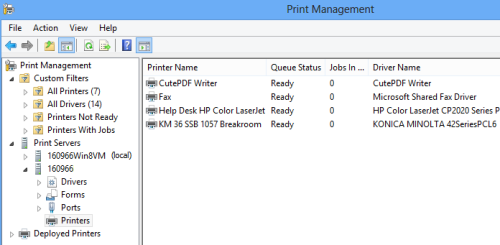
After establishing your remote session, list all printers installed on the target computer:
powershell
Get-PrinterThis command displays printer names, driver information, port details, and status. To see more detailed information about a specific printer:
powershell
Get-Printer -Name "Office Printer 01" | Format-List *Understanding which printers exist on the system helps you target the correct device when managing queues. Make note of the exact printer names, as they’re case-sensitive in some commands.
Step 4: Check the Current Print Queue Status
To view all jobs currently in a printer’s queue, use:
powershell
Get-PrintJob -PrinterName "Office Printer 01"This command shows each job’s ID number, document name, user who submitted it, status (printing, paused, error), and page count. The job ID is crucial for taking action on specific documents.
For a comprehensive view across all printers:
powershell
Get-Printer | ForEach-Object { Get-PrintJob -PrinterName $_.Name }This loop queries every printer and displays all pending jobs, helping you quickly identify where problems exist.
Step 5: Remove Stuck Print Jobs Remotely
When you need to clear specific jobs from the queue:
powershell
Remove-PrintJob -PrinterName "Office Printer 01" -ID 5Replace “5” with the actual job ID from the Get-PrintJob output. To clear all jobs from a printer at once:
powershell
Get-PrintJob -PrinterName "Office Printer 01" | Remove-PrintJobThis pipeline command retrieves all jobs and pipes them to the removal cmdlet. It’s the fastest way to clear a completely jammed queue.
For clearing queues on multiple printers simultaneously:
powershell
Get-Printer | Get-PrintJob | Remove-PrintJobUse this powerful command carefully, as it removes all print jobs from all printers on the system.
Step 6: Restart the Print Spooler Service Remotely
Sometimes printer queues won’t clear properly without restarting the Print Spooler service. To manage printer queues remotely using Windows PowerShell, you can restart services with these commands:
powershell
Restart-Service -Name SpoolerFor remote computers outside an active PowerShell session:
powershell
Invoke-Command -ComputerName RemotePC01 -ScriptBlock { Restart-Service Spooler }If jobs remain stuck even after clearing the queue, stop the spooler, delete temporary files, then restart:
powershell
Stop-Service Spooler
Remove-Item C:\Windows\System32\spool\PRINTERS\* -Force
Start-Service SpoolerThis process clears the physical spool folder where Windows stores print job data before sending it to the printer.
Step 7: Create Automated Monitoring Scripts
For ongoing printer management, create a PowerShell script that checks printer status automatically. Save this as Monitor-PrintQueues.ps1:
powershell
$Computers = "PC01","PC02","PC03"
$Results = @()
foreach ($Computer in $Computers) {
$Jobs = Invoke-Command -ComputerName $Computer -ScriptBlock {
Get-Printer | Get-PrintJob
}
if ($Jobs) {
$Results += [PSCustomObject]@{
Computer = $Computer
JobCount = $Jobs.Count
OldestJob = ($Jobs | Sort-Object SubmittedTime)[0].SubmittedTime
}
}
}
$Results | Where-Object { $_.JobCount -gt 10 } |
Format-Table -AutoSizeSchedule this script to run hourly using Task Scheduler. It identifies computers with more than 10 queued jobs, allowing proactive intervention before users complain.
Additional PowerShell Tools for Printer Management

Beyond queue management, PowerShell offers comprehensive printer administration capabilities. The Add-Printer cmdlet lets you deploy printers remotely:
powershell
Add-Printer -ConnectionName "\\PrintServer\OfficePrinter"You can also manage printer ports, which define how computers communicate with printers:
powershell
Get-PrinterPort
Add-PrinterPort -Name "IP_192.168.1.100" -PrinterHostAddress "192.168.1.100"For changing printer settings remotely, use Set-PrintConfiguration:
powershell
Set-PrintConfiguration -PrinterName "Office Printer 01" -DuplexingMode TwoSidedLongEdgeThese tools complement queue management by giving you full control over the entire printing infrastructure. The Microsoft documentation at <a href=”https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/module/printmanagement/”>https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/module/printmanagement/</a> provides detailed reference information for all PrintManagement cmdlets.
Common Mistakes and Troubleshooting Tips
Permission Errors When Connecting Remotely
If you receive “Access Denied” errors, verify that your account has administrator privileges on the target computer. Remote printer management requires local admin rights. Add your account to the local Administrators group or use domain admin credentials.
For workgroup environments, you may need to adjust Windows Firewall rules to allow WinRM traffic. Run this command on target machines:
powershell
Enable-NetFirewallRule -DisplayGroup "Windows Remote Management"Cmdlet Not Recognized Errors
If PowerShell doesn’t recognize printer cmdlets, the PrintManagement module may not be loaded. Import it manually:
powershell
Import-Module PrintManagementOn Windows 10 and Server 2016 or later, this module loads automatically. Older systems may require installing the Print Server role or RSAT tools.
Jobs Won’t Clear Despite Running Remove Commands
Persistent jobs often indicate corruption in the spool folder. Stop the spooler service, manually delete files from C:\Windows\System32\spool\PRINTERS\, then restart the service as shown in Step 6. Some stubborn jobs also require restarting the computer.
Check printer driver issues by examining event logs:
powershell
Get-EventLog -LogName System -Source "Print" -Newest 50Corrupted drivers frequently cause recurring queue problems. Reinstalling the printer driver may be necessary.
Remote Commands Time Out
Network latency or firewall configurations can cause timeouts. Increase the timeout value:
powershell
$SessionOption = New-PSSessionOption -IdleTimeout 300000
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName RemotePC01 -SessionOption $SessionOptionThis sets a 5-minute timeout instead of the default. For computers across slow WAN links, you may need even longer timeouts.
Cannot Find Printer Name
Printer names must match exactly, including spaces and special characters. Use tab completion after typing part of the name, or enclose names with spaces in quotes:
powershell
Get-PrintJob -PrinterName "HP LaserJet Pro M404"Running Get-Printer first to verify exact names prevents this common mistake.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can I manage printer queues remotely using Windows PowerShell on non-Windows printers?
Yes, as long as the printer is installed on a Windows computer, you can manage its queue remotely. PowerShell controls the Windows print queue, not the printer hardware directly. Network printers connected to Windows print servers work perfectly with these commands.
Q: Do I need special software to use PowerShell for remote printer management?
No additional software is required. PowerShell and the PrintManagement module come built into Windows 10, Windows 11, and Windows Server 2012 and later. You only need administrator credentials and network connectivity to the target computers.
Q: How do I manage printer queues on multiple computers at once?
Use the Invoke-Command cmdlet with an array of computer names. For example: Invoke-Command -ComputerName PC01,PC02,PC03 -ScriptBlock { Get-PrintJob | Remove-PrintJob } clears all queues on three computers simultaneously.
Q: Will clearing the print queue remotely delete documents permanently?
Yes, removing jobs from the queue deletes them. Users will need to resubmit documents. Always communicate with users before clearing active print jobs, as they may contain important work.
Conclusion

Learning to manage printer queues remotely using Windows PowerShell transforms printer support from a time-consuming physical task into an efficient remote operation. The seven steps outlined in this guide provide everything you need to view queues, clear stuck jobs, restart services, and automate monitoring across your network. Start with basic commands like Get-Printer and Remove-PrintJob, then gradually build more sophisticated scripts as your confidence grows. Remote printer management not only saves time but also improves user satisfaction by resolving printing issues faster than ever before. Implement these PowerShell techniques today and experience the productivity gains that come from centralized, automated printer administration.